The year 2020, plagued by the Covid-19 pandemic, has passed. European countries suffered amid the coronavirus’s spread, with Italy, Spain, the United Kingdom, and France most negatively affected in the first wave. Subsequently, during the second wave, the United Kingdom and Portugal ended up leading in infection rates and discovering a new yet more contagious strain.
Despite the ailments and suffering caused by the disease, the management and control authorities protecting personal data have not been idle. At the end of the twelve months, the member countries of the European Economic Area (comprising the following countries: Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Croatia, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Estonia, Finland, France, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Czech Republic, Romania, and Sweden) and the United Kingdom, now outside the EEA after Brexit, but still covered under the European Data Protection Law (GDPR), reached three hundred and twenty-three (323) penalties, amounting to a total of € 170,329,328.00.
Drawing on the data presented above, it is possible to produce the graph below, which reveals that the pandemic has dramatically affected the economy and national personal data protection authorities’ performance in their respective countries. This can be seen most clearly in the sharp drop in the number and value of penalties during March, April, and May when several European countries were undergoing lockdown. When the pandemic seemed to retreat, more action was taken by national personal data protection authorities, especially in June and July. With the second wave’s arrival, another significant reduction in the number and value of penalties occurred in August and September. However, October registered a substantial increase in the value of penalties, especially in the fines levied by the Information Commissioner’s Office of the United Kingdom (ICO), on British Airways (for € 22,046,000.00) and Marriott International Inc. (for € 20,450 .000,00) and by the Hamburgische Beauftragte für Datenschutz und Informationsfreiheit (HmbBfDI) in Germany, against H&M Hennes & Mauritz Online Shop AB & Co. KG (for € 35,258,708.00). November and December were months in which the authorities intensified the number of penalties, respectively, 29 and 46, although the fines were not as significant.
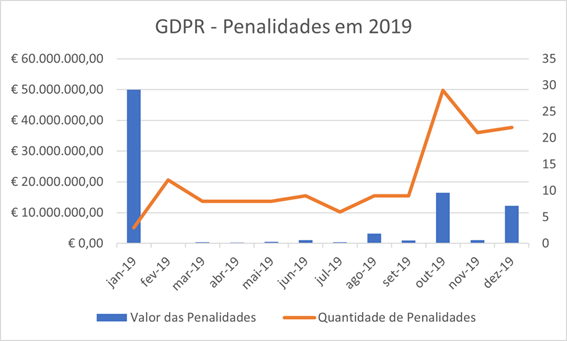
An important point to consider is the difference between the totals for 2019 and 2020. In 2019, the penalties applied by the national data protection authorities of the EEA countries and the United Kingdom reached one hundred and forty-four (144) penalties, resulting in fines of € 86,859,914.00.
Finally, it is noteworthy that, despite the pandemic, the EEA and the United Kingdom’s national data protection authorities more than doubled the value and number of penalties in 2020, compared to the totals registered in 2019.

